The benefits of the blood type diet have become increasingly popular as individuals look to enhance their health through tailored nutrition. This diet is based on the premise that different blood types respond uniquely to various foods.

Advocates suggest that by aligning your eating habits with your blood type, you may experience better health, weight loss, and overall wellness. In this article, we’ll delve into the principles of the blood type diet, examine its potential benefits and drawbacks, and offer practical tips for incorporating it into your lifestyle.
What is a Blood Type Diet?
The blood type diet was popularized by Dr. Peter D’Adamo in his book “Eat Right 4 Your Type,” published in 1996. The premise is straightforward: each blood type (A, B, AB, and O) has specific dietary needs and recommendations based on the biochemical properties of the blood.
According to D’Adamo, consuming foods that align with your blood type can enhance your health, boost your immune system, and promote weight loss.
The Four Blood Types and Their Diets
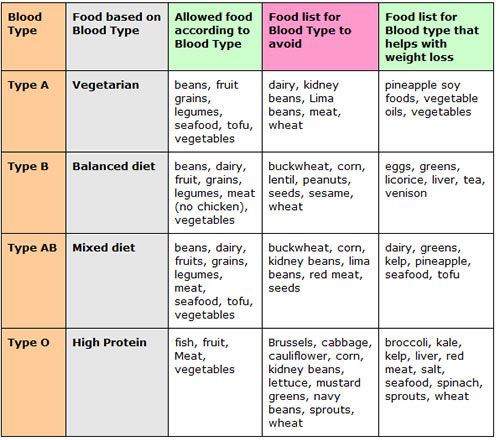
- Type A: Often called the “Agrarian” or “Cultivator” diet, individuals with type A blood are encouraged to follow a vegetarian or plant-based diet. The focus is on fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. Type A individuals should avoid red meat and focus on fish and poultry instead.
- Type B: Known as the “Nomad” diet, type B individuals are said to thrive on a diverse diet that includes meat (except chicken), dairy, and a variety of vegetables. They should avoid certain foods like corn, wheat, and peanuts.
- Type AB: As a mix of both A and B types, individuals with type AB blood are encouraged to eat a combination of both diets. This includes seafood, tofu, dairy, and green vegetables while avoiding smoked and processed meats.
- Type O: Known as the “Hunter” diet, type O individuals are advised to consume a high-protein diet rich in lean meats, fish, vegetables, and fruits while avoiding grains, legumes, and dairy products.
The Science Behind the Benefits of Blood Type Diet
The benefits of the blood type diet have attracted many followers, but it’s essential to understand that scientific evidence supporting its effectiveness is limited. Some studies indicate that blood type may affect certain health factors, such as vulnerability to specific diseases or how the body processes different foods. However, more comprehensive and rigorous research is needed to establish a definitive connection between blood type and dietary requirements.
Despite the lack of conclusive scientific evidence, numerous individuals report experiencing positive outcomes from the blood type diet. Many claim to have improved digestion, increased energy levels, and weight loss after tailoring their eating habits to their blood type. These personal stories can serve as powerful motivators, even when scientific support is minimal.
Pros of a Blood Type Diet
- Personalized Nutrition: One of the primary appeals of a blood group diet is the notion of personalized nutrition. By tailoring your diet to your specific blood type, you may find that certain foods work better for your body than others.
- Increased Awareness of Food Choices: Following a blood type diet encourages individuals to be more mindful of their food choices, promoting healthier eating habits overall. This can lead to improved nutrient intake and better health outcomes.
- Emphasis on Whole Foods: The Blood group nutrition plan promotes the consumption of whole, unprocessed foods, which can have numerous health benefits. Incorporating fresh fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins into your diet can help you feel better and may support weight management.
- Potential for Weight Loss: Many people report weight loss after starting a blood type diet. This may be due to the focus on whole foods and the elimination of processed foods, rather than the specific blood type recommendations.
- Flexibility in Food Choices: The blood type diet allows for a range of food choices within each blood type category, making it relatively flexible compared to other restrictive diets. This can make it easier to sustain in the long run.
Cons of a Blood group nutrition plan
- Lack of Scientific Evidence: One of the main criticisms of the blood type diet is the lack of substantial scientific research supporting its effectiveness. Many nutrition experts argue that dietary recommendations should be based on individual needs, rather than blood type alone.
- Potential Nutritional Deficiencies: Strict adherence to the blood type diet may lead to nutritional deficiencies, particularly if certain food groups are eliminated. For example, type A individuals may miss out on essential nutrients found in animal products if they strictly follow a vegetarian diet.
- Overgeneralization: Blood type alone does not account for individual differences in metabolism, lifestyle, and health conditions. Two people with the same blood type may have vastly different dietary needs based on factors like age, activity level, and existing health issues.
- Exclusion of Healthy Foods: The blood group nutrition plan may label certain healthy foods as “off-limits” based on blood type, which can lead to unnecessary food restrictions. For example, whole grains and legumes are beneficial for most people, but type O individuals are advised to avoid them.
- Complexity and Confusion: The guidelines for each blood type can be complex and confusing for some individuals. This may lead to frustration and difficulty in implementing the diet effectively.
Tips for Implementing a Blood Group Diet
If you’re interested in trying a blood group nutrition plan here are some tips to help you get started:
- Know Your Blood Type: The first step is to determine your blood type. You can do this through a blood test at your doctor’s office or use a home testing kit.
- Educate Yourself: Read books and resources about the blood type diet to understand the specific recommendations for your blood type. Familiarize yourself with the foods you should emphasize and those to avoid.
- Start Slowly: If you’re transitioning to a blood group nutrition plan, start slowly by incorporating more foods that align with your blood type while gradually reducing those that don’t. This can make the transition smoother and more manageable.
- Focus on Whole Foods: Regardless of blood type, prioritize whole, nutrient-dense foods. Fresh fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats should be the foundation of your diet.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to how your body responds to different foods. If you notice that certain foods, even those recommended for your blood type, cause discomfort or digestive issues, it’s essential to adjust accordingly.
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: Before making significant dietary changes, it’s a good idea to consult with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional. They can help you tailor the blood type diet to your specific needs and ensure you’re meeting your nutritional requirements.
Conclusion
A blood type diet offers a unique approach to nutrition that emphasizes personalized eating based on your blood type. While it may not be universally supported by scientific research, many individuals report positive experiences and health benefits from following the diet.
Before diving into the blood group nutrition plan, it’s essential to weigh the pros and cons of a blood type diet and consider whether it aligns with your individual health goals and lifestyle. By focusing on whole foods and being mindful of your body’s responses, you can find a dietary approach that works for you. Whether or not you choose to follow a blood type diet, remember that the key to optimal health lies in a balanced and varied diet tailored to your individual needs.
